Under Construction
Software and network setup
This section contains material about installing necessary drivers, initializing the modem, configuring software settings, and establishing network connectivity with RM530N-GL on a Raspberry Pi board.
Important note:
We will be establishing a network ✅ over a USB connection from RPi-5 and the RM530N-GL cap. (we are ❌ NOT using PCIe connection)
1. Check the hardware connectivity
Before we start working on the software, we need to make sure that hardware mounting and connectivity is correct.
- USB cable is connected
- Cap is mounted properly.
- Antenna is mounted on the cap and wires are connected properly.
For detailed connection information, see the hardware setup
2. USB connectivity
Power-on the RPi-5 board with the cap mounted on.
Check USB detection
There appears a list of usb devices, and if quectel modem is detected, we should see an entry like this:Check serial ports (ttyUSB)
OR monitor while plugging in We should see entries like this:usb 1-1: GSM modem (1-port) converter now attached to ttyUSB0
usb 1-1: GSM modem (1-port) converter now attached to ttyUSB1
usb 1-1: GSM modem (1-port) converter now attached to ttyUSB2
usb 1-1: GSM modem (1-port) converter now attached to ttyUSB3
usb-device list (optional)
type
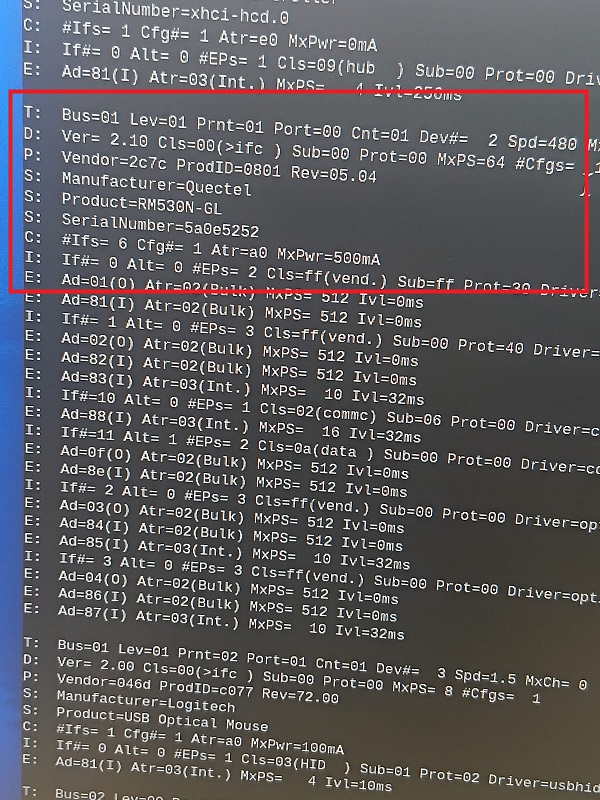
Information about Quectel and device model RM50N-GL should be display (click to enlarge):Note: Quectel modems usually expose multiple interfaces, each for different purposes: (for AT command setup, we'll be using ttyUSB2)
3. Run NetworkManager service
NetworkManager service runs automatically at bootup. However, sometime we might have disabled it for some reason.
systemctl status NetworkManager #check the status
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager #start the service if not already running
sudo systemctl enable NetworkManager #this will cause the service to start at bootup
4. Install minicom
Minicom:
- is a text-based serial communication tool (terminal emulator) for Linux
- is a lightweight alternative to tools like PuTTY.
To install:
To verify:
We should see something like this:
5. Configure Quectel modem
⚠️ Stop ModemManager (MM) service
We have to stop the ModemManager service, because MM uses same usb channels as used by minicom, and we'll encouter unwanted behaviour.
Type this to stop the service
✅ Configure modem via AT commands
AT commands are the universal language to interact with and control cellular modems (provided by the modem vendors like quectel)
Step 1: Start Minicom
type any one of the following:
Or connect without mentioning the baudrate (minicom uses 115200 as default)(This section and after this are still under construction...following is just for my own refrence to complete this page..later on will be adjusted properly)
Step 2: Configure telco connectivity
- activate sim
- connect to APN and get IP
- create a TCP connection
Note: Check APN Automatically (if supported) AT+QICSGP=1,1
or activate without APN AT+QIACT=1
or set "sunsurf" for M1
Step 3: Configure USB interface
- change device mode
- switch from PCIe to USB
AT+QCFG="data_interface",0,0
This sets: (as in the pdf reference document)
Protocol = ECM (0) → Ethernet-over-USB
Mode = default (0) → one USB function exposed as ECM (likely usb0)
AT+QCFG="usbnet",1 (default was 2, which didn't work)
AT+CFUN=1,1 ( to reboot the modem)
must verify following modes' values' (use lsmod because every source has diffeent info
| Value | Mode | Interface Name | Kernel Driver | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ECM | usb0 | cdc_ether, usbnet | Simple, widely supported |
| 1 | MBIM | wwan0 | cdc_mbim, usbnet | Modern, efficient, preferred |
| 2 | RNDIS | usb0 | rndis_host | Windows-friendly, less common on Linux |
| 3 | NCM | usb0 or wwanX | cdc_ncm | High-performance alternative |
| 5 | QMI | wwanX | qmi_wwan | For use with libqmi or qmicli |
Detailed AT Commands Reference
6. Test internet connection
- Check network interface
- ping and internet access
7. Setup modem manager
- setup DNS
add a link to MManager tutorial
For detailed introduction to MM: Modem Manager in detail
8. Index
Com port functions (ttyUSB*)
The com port recognized by the module acts as follows:
| Device/Port | Description |
|---|---|
| /dev/ttyUSB0 | DIAG Port for output developing message |
| /dev/ttyUSB1 | NMEA Port for GNSS NMEA data output |
| /dev/ttyUSB2 | AT Port for AT Commands |
| /dev/ttyUSB3 | Modem |
Internet access modes
**important:" use lsmod to verify (different information at different places)
| Command | Driver Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AT+QCFG="usbnet",0 | NDIS (QMI) | Driver type is NDIS (QMI) |
| AT+QCFG="usbnet",1 | ECM | Driver type is ECM (recommended for Linux) |
| AT+QCFG="usbnet",2 | MBIM | Driver type is MBIM (recommended for Windows, not supported for Linux) |
| AT+QCFG="usbnet",3 | RNDIS | Driver type is RNDIS (recommended for Linux) |
| AT+QCFG="usbnet",5 | NCM | Driver type is NCM (not supported for Linux) |
USB vs PCIe mode selection
Ref: Quectel_AT_Commands_Manual_PDF
at+qcfg="data_interface",1,0 at+qcfg="data_interface",0,0
put explaination from the above PDF file This sets: (as in the pdf reference document) Protocol = ECM (0) → Ethernet-over-USB Mode = default (0) → one USB function exposed as ECM (likely usb0)
9. Some useful links
Detailed AT Commands Reference